What is Wholesale Distribution?
Wholesale distribution refers to the process of buying products directly from manufacturers before selling them to retailers and other commercial businesses.
Wholesalers effectively act as intermediaries between manufacturing businesses and organisations other than the end user. This usually involves purchasing bulk orders of certain products at a discounted ‘wholesale’ price, then selling those goods in smaller quantities at a higher markup.
Interested in learning more about wholesale and distribution? This guide explores the world of wholesale distribution - strategies, systems, future trends and essential concepts for success.

What are Wholesale Distribution Systems?
Wholesale distribution systems enable wholesalers to manage each stage of the purchasing and distribution process, from order processing and stock management to delivery tracking, customer service and invoicing.
Intuitive analytics functions and real-time data dashboards make it easier for managers to highlight trends, flag up issues and get a clearer view of business performance. These insights often help inform strategic decisions and keep operations running at maximum efficiency, for better cash flow.
Wholesale distribution software can serve the needs of both small and large-scale operations, such as dairy and foodservice, with varying methods of distribution.
Some solutions offer easy integration with payments and accounting systems, allowing teams to work from a single source of data and cutting down time-consuming admin and potential human error. It also helps businesses get paid faster.
Self-service capability and process automation also frees up time for employees to focus on more important tasks, while still providing an engaging service experience for both staff and customers.
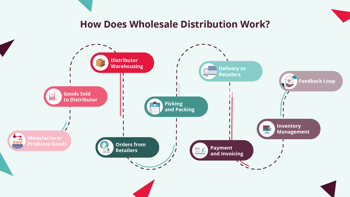
How Does Wholesale Distribution Work?
There are a number of moving parts involved in the wholesale distribution process, each one a crucial component of a robust supply chain. Ongoing management and optimisation of each step is important to reduce the risk of issues or delays, while keeping stakeholders, staff and customers satisfied and on the same page.
Here are the main stages:
Here are the main stages:
Why is Wholesale Distribution Important?
Wholesale distribution plays an integral role in the overall operational efficiency of various industries and local economies, helping to streamline supply chains and reduce costs and ensuring manufacturers get their product lines to market efficiently.
Unlike manufacturers, distributors tend to maintain large retail networks and extensive logistics operations, allowing them to reach locations and businesses that would be far more difficult or costly for manufacturers.
In addition to delivery networks, distributors also often have extensive warehouse spaces in which they store products, which eases the burden on storage for manufacturers and also gives retailers and commercial business access to a diverse selection of goods in smaller quantities.
Here are a few examples of industries that rely on effective wholesale distribution:
- Food and beverage – Food service wholesalers need to demonstrate ongoing compliance with strict hygiene, storage and distribution standards. They supply a wide range of clients, from restaurants and cafes to grocery stores and venues.
-
Consumer goods and electronics – Distributors are a vital cog in electronics supply chains, supplying inventory to high street retailers and appliance specialists while also meeting rapidly shifting technology trends and retailer demands.
-
Healthcare and pharmaceuticals – As with food and beverage, medical distributors must adhere to strict storage and transportation regulations when partnering with hospitals, clinics and other healthcare organisations.
-
Construction – Construction projects require a wide range of specialist materials and equipment. Distributors act as a one-stop-shop for construction companies, providing convenient access to materials such as timber, concrete, steel, fixtures, electrical components without needing to source these individually from manufacturers and suppliers.
The benefits of an efficient wholesale distribution system
- Automate processes such as order management, inventory tracking, invoicing, and shipping. This streamlines operations and reduces manual errors
- Optimise inventory levels, reducing carrying costs while ensuring adequate stock availability. Reduce order processing times, which improves customer satisfaction
- Increase visibility across the entire supply chain – this helps you identify bottlenecks and issues and take action; you can make faster and better informed decisions based on accurate data, and improve responsiveness
- Reduce costs by improving operational efficiency, for example better labour allocation and use, and reduced errors, returns, and stockouts
- Achieve compliance through traceability functionality, automated checks and reporting
Wholesale Distribution Strategies
No matter the type of distribution you specialise in, a clear strategy is essential to manage the continual flow of goods from manufacturers to retailers and end consumers without any major interruptions.
It’s worth noting that wholesale distribution strategies are not mutually exclusive; in fact, successful wholesalers often combine approaches to create a comprehensive business model that can adapt to changing circumstances.
Bulk Purchasing
Bulk purchasing involves buying large quantities of products from manufacturers or suppliers at discounted prices. This strategy allows wholesalers to take advantage of economies of scale and lower per-unit costs, negotiating better deals due to the high volume of goods purchased.
Just-in-Time Inventory (JIT)
Just-in-time inventory management focuses on minimising inventory holding costs by ordering goods only when they are needed for fulfilment. Wholesalers use this strategy as a way to minimise warehousing costs and the risk of obsolete inventory.
Specialisation
Some distributors specialise in specific product categories or customer segments, marketing their services to particular niches with certain demands or required expertise. This can be a good way to differentiate from rivals, build strong relationships with customers and command premium prices for a specialised service.
Value-Added Services
Value-added services go beyond the basic distribution of products and include additional benefits such as customisation, packaging, labelling, technical support or after-sales services.
E-Commerce Integration
E-commerce integration involves leveraging online platforms and technologies to ease the buying and selling processes. Wholesalers can adopt e-commerce channels to reach a broader customer base, streamline order processing and provide convenience to customers through online ordering and self-service tools.
Collaborative Planning
Collaborative planning strategies involve working closely with suppliers, customers and other stakeholders to forecast demand, optimise inventory levels and improve overall supply chain efficiency. This may be through joint forecasting, sharing of information or coordinated decision-making processes with their partners.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Wholesalers using CRM strategies gather customer data, analyse preferences and tailor their services to meet individual needs. By building greater trust and loyalty, CRM enhances customer satisfaction, retention and long-term profitability for wholesalers.
What is the Future of Wholesale Distribution?
“We’re already seeing huge transformative shifts in the distribution sector driven by technology. Artificial intelligence, automation and data analytics are helping wholesalers to streamline operations further and enhance efficiency and accuracy across each stage of their supply chain. Stronger collaboration between distributors and manufacturers is also developing – and both sides face the challenge of becoming more agile and responsive to customer demands.”
“E-commerce integration is likely going to continue growing, helping to provide a seamless buying and selling experience for distributors. Sustainability and environmental considerations will play an even bigger role, which is why digitising audit trails is so important to demonstrate compliance whenever needed.”
– Amy Fallon, Wholesale and Distribution Software Specialist, The Access Group
Wholesale Distribution Glossary
|
Wholesaler |
A business that purchases goods in large quantities from manufacturers and sells them in smaller quantities to retailers. |
|
Distributor |
An intermediary between manufacturers and retailers that purchases, stores, and sells goods in bulk to retailers. |
|
Supply House |
A business that stocks and supplies a wide range of products for various industries and retailers. |
|
Importer/Exporter |
A business involved in bringing goods into a country (importer) or sending goods to another country (exporter) for sale. |
|
Master Distributor |
A distributor that holds a unique position in the distribution channel, often serving as a key intermediary between manufacturers and other distributors. |
|
Buying/Selling Group |
An organisation or association formed by retailers or wholesalers to leverage collective purchasing power for better deals and discounts from suppliers. |
|
Trading Companies |
Businesses that facilitate international trade by buying and selling goods, often acting as intermediaries between buyers and sellers in different countries. |
Discover Cutting-Edge Wholesale Distribution Software
Wholesalers today face a host of challenges and opportunities for growth –only those who have the right digital infrastructure in place will be able to stay at the front of the pack.
Wholesale distribution software can unlock the full potential of your operations by enabling you to efficiently track, plan and automate key processes and drivers of efficiency. Having a scalable, end-to-end system at the centre of your business can make all the difference when it comes to achieving seamless workflows and ensuring depot staff, drivers and office-based employees stay connected.
Customer expectations are ever growing, and meeting these in an agile way is critical.
Wholesale Distribution FAQs
How can businesses ensure compliance with environmental regulations through wholesale distribution?
Environmental regulations are continually evolving, and distributors must be able to demonstrate compliance and traceability at all times. An intuitive wholesale distribution system makes it more simple to conduct regular audits and assessments in line with compliance guidelines, while also flagging potential high-risk areas.
What role does technology play in optimising wholesale distribution processes for organisations?
Modern wholesalers rely heavily on digitised processes and automation to reach the highest levels of productivity. Whether it’s inventory management, order processing, data analytics or reporting, technology is now an integral part of operations to deliver on the demands of local, national or global supply chains.
Do wholesale distributors sell to the public?
Most wholesale distributors primarily sell goods in bulk quantities to retailers and businesses, rather than directly to the public. While most have minimum order requirements or membership programs for access to their products, certain wholesalers may offer retail services through separate channels or subsidiaries, allowing them to serve both wholesale and retail markets.

